Differences Between Heart Attack and Stroke
Introduction
Understanding the distinctions between a coronary failure and a stroke is significant, as both are health related crises that require quick consideration yet include various pieces of the body and present various side effects.
Heart Attack:
A coronary episode, otherwise called a myocardial localized necrosis, happens when the blood stream to a piece of the heart muscle is obstructed, generally by a blood coagulation. This can occur because of an impeded vein (ischemic stroke) or a burst vein (hemorrhagic stroke). The absence of blood stream denies mind tissue of oxygen and supplements, prompting the demise of synapses.
Side effects
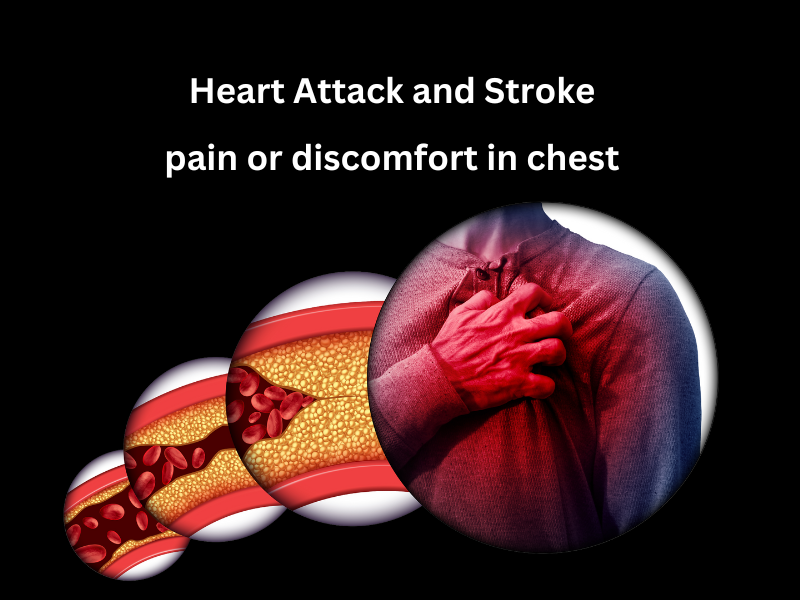
Respiratory failure:
Chest torture or burden is every now and again depicted as strain, squeezing, or culmination.
Torture or disquiet in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach
Shortness of breath
Cold sweat, nausea, or unsteadiness
Stroke:
Surprising deadness or weakness, especially on one side of the body
Chaos, bother talking, or sorting out talk
Inconvenience tracking down in one or the two eyes
Bother walking, confusion, loss of balance, or coordination
Serious cerebral torment with not a great explanation
Cause
A respiratory failure, or myocardial localized necrosis, happens when the blood stream to a piece of the heart muscle is hindered, prompting harm or demise of heart tissue. The essential drivers of a respiratory failure include:
- Coronary conduit sickness (CAD) : This is the most widely recognized reason for coronary episodes. It happens when the coronary courses, which supply blood to the heart muscle, become restricted or hindered by greasy stores called plaques (atherosclerosis).
- Blood clots : A burst in a plaque can set off the development of a blood coagulation, which can impede the progression of blood through the coronary corridor, causing a cardiovascular failure.
- Spasm of coronary arteries. In some cases, an unexpected fit in a coronary supply route can limit bloodstream to the heart. This fit can be set off by drug use (like cocaine), intense pressure, or openness to cold.
4..Excessive liquor consumption : Weighty drinking can prompt hypertension, stoutness, and harm to the heart muscle, raising the gamble of a respiratory failure.
- Family history of heart disease : In the event that direct relations have had coronary illness or respiratory failures, there might be a hereditary inclination to comparative circumstances.
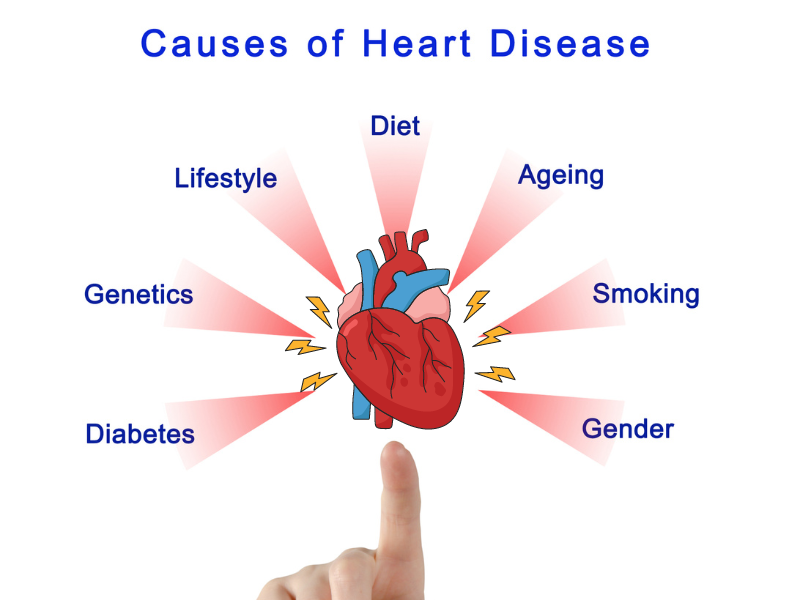
Risk Variables
Coronary failure: Hazard factors incorporate hypertension, elevated cholesterol, smoking, weight, absence of active work, diabetes, and a family background of coronary illness.
Stroke: Hazard factors incorporate hypertension, atrial fibrillation (a sporadic heartbeat), diabetes, elevated cholesterol, smoking, stoutness, and a family background of stroke.
Treatment
Coronary episode: Quick treatment centers around reestablishing bloodstream to the heart muscle. This might include prescription like anti-inflammatory medicine, thrombolytic s (cluster busting medications), or methodology like angioplasty and stinting.
Stroke: Treatment relies upon the kind of stroke. For ischemic stroke, cluster busting drugs (thrombolytic s) might be utilized to reestablish blood stream. At times, mechanical thrombectomy, a methodology to eliminate the coagulation, might be performed. For hemorrhagic stroke, treatment includes controlling draining and lessening tension in the cerebrum.
Prevention
Coronary episode: Preventive estimates integrate keeping a sound eating routine, rehearsing reliably, going without smoking, supervising pressure, and controlling beta factors like circulatory strain, cholesterol, and diabetes.
Stroke: Relative preventive measures apply, for instance, directing heartbeat, cholesterol, and diabetes, halting smoking, eating a strong eating schedule, and remaining genuinely unique. Furthermore, overseeing atrial fibrillation with medicine can lessen the gamble of stroke.
While both coronary episodes and strokes are extreme circumstances that include the interference of blood stream to basic organs, they contrast in their causes, side effects, and treatment. Understanding these distinctions can assist with perceiving the side effects early and look for brief clinical consideration, which is imperative for further developing results and endurance rates.